What’s different?
Electroplating and electroless plating are both methods of coating a material or a component with a layer of metal, thereby protecting and strengthening the core component, helping it to resist moisture, increasing its lasting power and preventing corrosion. These two methods both have their own distinct advantages and drawbacks.
Electroplating
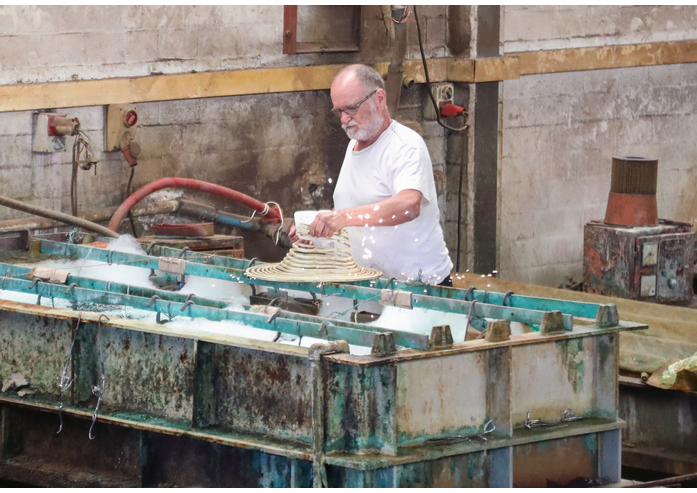
The main difference between these two methods is the use of an electrical current, which as its name suggests, does not occur in electroless plating. In electroplating, electricity is used to coat the component.

First, it’s cleaned and dried to ensure there’s no debris or dust on its surface, then it’s usually submerged in an electrolyte solution along with the metal plating particles. An electrical current is applied which causes the metal plating particles to bind to the component’s surface. For an in-depth explanation of this method, see here.
Electroless Plating
Unlike electroplating, electroless plating doesn’t rely on electricity. Instead, the component and its metal coating are bound together solely by a chemical reaction, e.g. in electroless nickel plating.
The object is treated with chemicals in a catalytic solution to induce oxidation. Although it sounds complicated, this chemical reaction simply causes the metal plating material to bind to and coat the object. For those seeking electroless nickel plating, a specialist such as www.poeton.co.uk/standard-treatments/electroless-nickel-plating/ offers a variety of solutions.
Which method is for me?
Electroplating excels if your object requires a thicker metal coating as electroless plating typically provides a slightly thinner coating than its counterpart. This makes it an ideal option for objects or components that need exceptional protection against corrosion, for example, those used in the aerospace or automotive industries.
However, electroless nickel plating allows for a more uniform coating overall, which is more difficult to achieve using the electroplating method. This makes it the stand-out choice for coating jewellery, circuit boards, electronics and delicate components.

Another key factor is the conductivity of the component you’re looking to coat. Electroplating requires the item to be conducive, that is, to conduct electricity. Electroless plating, however, can be used to coat any object, offering additional versatility.